SWOT analysis is a popular tool among businesses and is often used to evaluate a new business venture, product or service, or to analyze the performance of an existing organization. It can be used by small and large businesses, non-profit organizations, and government agencies.
Elements of a SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis consists of four key elements, as follows:
Strengths: These are the internal factors that contribute to the success of an organization. They may include unique skills and knowledge possessed by the organization, strong relationships with key stakeholders, advanced technology, and financial stability.
Weaknesses: These are the internal factors that limit an organization's success. They may include lack of experience, poor management, inadequate financial resources, and a limited product or service portfolio.
Opportunities: These are external factors that can benefit an organization. They may include new markets, changes in consumer trends, technological advancements, and economic growth.
Threats: These are external factors that can harm an organization's performance. They may include competition, regulatory changes, economic recession, and changing consumer preferences.
To conduct a SWOT analysis, an organization typically forms a team of key stakeholders, including employees, managers, and external consultants. The team then conducts a thorough analysis of each of the four elements, using a variety of methods such as surveys, interviews, and data analysis. The team then develops a comprehensive report summarizing the findings of the analysis and recommending strategies to address the identified issues.
SWOT table
A SWOT table is a visual representation of a SWOT analysis. It is a four-quadrant table that lists the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of an organization. Here is an example of a SWOT table:
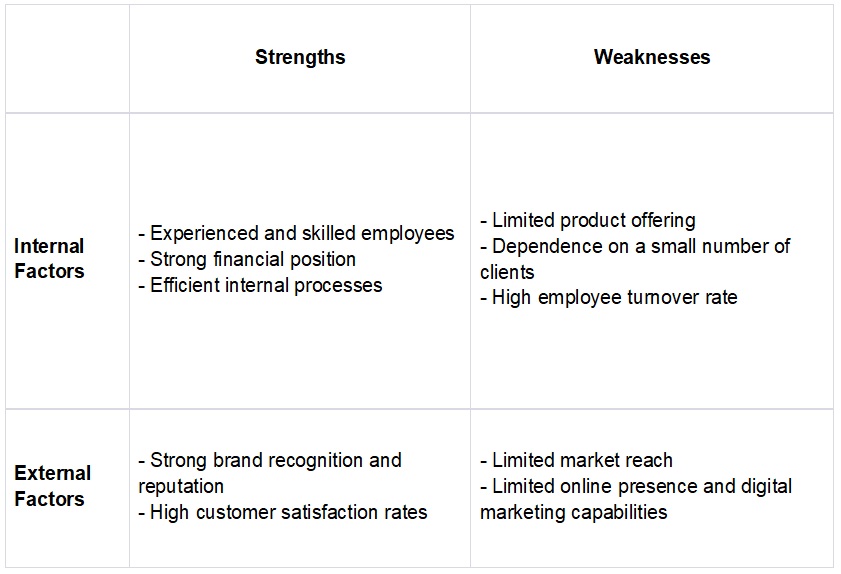
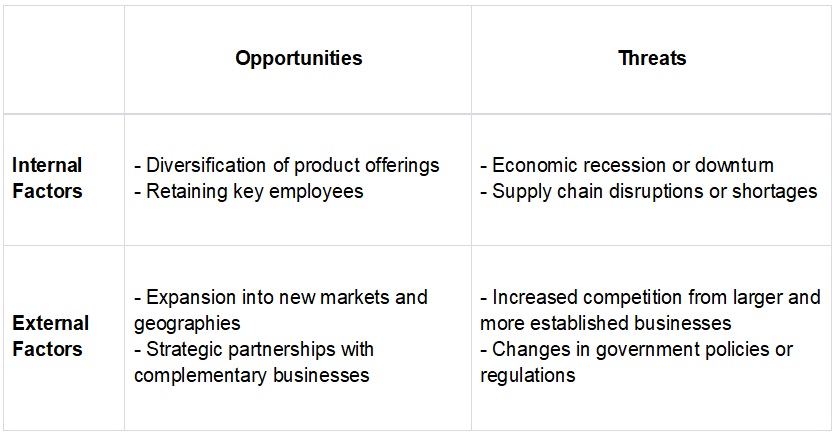
In this example, the SWOT table is divided into four quadrants, with the strengths and weaknesses listed in the top row and the opportunities and threats listed in the bottom row. The left column represents the internal factors, such as the organization's employees and internal processes, while the right column represents the external factors, such as the organization's brand recognition and the market environment. Each factor is listed in a separate cell in the appropriate quadrant.
The SWOT table provides a visual overview of the organization's internal and external environment, making it easy to identify the key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This information can be used to develop strategies to capitalize on the strengths, address the weaknesses, take advantage of the opportunities, and mitigate the threats.
How to do a SWOT analysis
To conduct a SWOT analysis, follow these steps:
- Define the objective: Identify the objective of the analysis, such as evaluating a new business venture, assessing the performance of an existing organization, or developing a new product or service.
- Gather data: Collect relevant data about the organization, including financial reports, market research, customer feedback, and employee surveys.
- Identify strengths: List the internal factors that contribute to the success of the organization. This can include unique skills and knowledge possessed by the organization, strong relationships with key stakeholders, advanced technology, and financial stability.
- Identify weaknesses: List the internal factors that limit the organization's success. This can include lack of experience, poor management, inadequate financial resources, and a limited product or service portfolio.
- Identify opportunities: List the external factors that can benefit the organization. This can include new markets, changes in consumer trends, technological advancements, and economic growth.
- Identify threats: List the external factors that can harm the organization's performance. This can include competition, regulatory changes, economic recession, and changing consumer preferences.
- Analyze the data: Analyze the information gathered in steps 3-6 to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between the various factors.
- Develop strategies: Use the analysis to develop strategies to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, take advantage of opportunities, and mitigate potential threats. This can include developing new products or services, expanding into new markets, improving internal processes and systems, or building strategic partnerships.
- Review and revise: Regularly review and revise the SWOT analysis as the organization evolves and its internal and external environment changes.
Overall, conducting a SWOT analysis requires a comprehensive understanding of the organization's internal and external factors, as well as a strategic mindset to develop effective strategies to achieve its objectives.
SWOT analysis example
Here is an example of a SWOT analysis for a hypothetical small business:
Strengths:
- Strong brand reputation and recognition
- Experienced and skilled team of employees
- Efficient internal processes and systems
- Strong financial position with a solid cash reserve
- High customer satisfaction rates
Weaknesses:
- Limited product offering
- Limited market reach
- Limited online presence and digital marketing capabilities
- High employee turnover rate
- Dependence on a small number of key clients
Opportunities:
- Expansion into new markets and geographies
- Diversification of product offerings
- Increased investment in digital marketing and online presence
- Development of strategic partnerships with complementary businesses
- Acquisition of a smaller competitor to increase market share
Threats:
- Increased competition from larger and more established businesses
- Economic recession or downturn
- Changes in government policies or regulations
- Shifts in consumer preferences and behavior
- Supply chain disruptions or shortages
Based on this SWOT analysis, the small business could consider developing new products to expand its offering, investing in digital marketing to increase its online presence and reach new customers, and exploring partnerships with other businesses to expand its market reach. It could also consider acquiring a smaller competitor to increase its market share and mitigate the threat of increased competition. Additionally, it could focus on retaining key employees and diversifying its client base to address its weaknesses.
Why is SWOT analysis used?
SWOT analysis is a widely used tool in business and management for analyzing an organization's internal and external environment to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here are some reasons why SWOT analysis is used:
- Strategic planning: SWOT analysis is often used as part of the strategic planning process to inform decisions about the organization's future direction, objectives, and priorities.
- Business development: SWOT analysis can help businesses identify new opportunities for growth, such as entering new markets or developing new products or services.
- Risk management: SWOT analysis can help businesses identify potential threats and risks, such as changes in consumer behavior or economic downturns, and develop strategies to mitigate them.
- Performance evaluation: SWOT analysis can be used to evaluate the performance of the organization by identifying areas of strength and weakness that can be used to inform improvements.
- Competitive analysis: SWOT analysis can be used to compare the organization to its competitors and identify areas where it has a competitive advantage or is at a disadvantage.
- Investment analysis: SWOT analysis can be used by investors and financial analysts to evaluate the potential of an organization and inform investment decisions.
Overall, SWOT analysis is used to provide a comprehensive understanding of the organization's internal and external environment and inform strategic decision-making. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, SWOT analysis helps businesses and organizations make informed decisions that can lead to improved performance and long-term success.
How to write a good SWOT analysis
To write a good SWOT analysis, follow these tips:
- Be specific: Use specific examples and data to support each point in the analysis. Avoid vague or general statements that do not provide any real insight.
- Be honest: Identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of the organization honestly and objectively. Avoid exaggerating the positives or downplaying the negatives.
- Prioritize: Prioritize the factors in each category based on their level of importance and impact on the organization. This will help to focus on the most critical issues and opportunities.
- Be concise: Keep the analysis concise and to the point. Avoid including unnecessary details or information that does not contribute to the analysis.
- Provide context: Provide context for each factor by explaining how it relates to the organization's overall strategy and objectives.
- Use a structured format: Use a structured format to present the SWOT analysis, such as a table or matrix. This will help to organize the information and make it easier to understand.
- Link strengths to opportunities and weaknesses to threats: Link the strengths to the opportunities and the weaknesses to the threats. This will help to identify potential strategies that can leverage the strengths to take advantage of the opportunities or address the weaknesses to mitigate the threats.
- Develop strategies: Based on the SWOT analysis, develop strategies to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, take advantage of opportunities, and mitigate potential threats. These strategies should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Review and revise: Regularly review and revise the SWOT analysis as the organization evolves and its internal and external environment changes.
Overall, a good SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the organization's internal and external environment and identifies opportunities and challenges that can inform strategic decision-making.
Advantages of SWOT analysis
One of the major advantages of SWOT analysis is that it helps organizations to identify their unique strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to develop strategies that are tailored to their specific needs. By identifying their strengths, organizations can focus on leveraging those strengths to achieve their objectives. By identifying their weaknesses, organizations can take steps to address those weaknesses and improve their performance.
Another advantage of SWOT analysis is that it helps organizations to identify potential opportunities and threats in their external environment. This allows organizations to proactively develop strategies to take advantage of opportunities and mitigate potential threats. For example, an organization may identify a new market opportunity that they can capitalize on, or they may identify a potential regulatory change that could negatively impact their business. By identifying these opportunities and threats early on, organizations can take proactive steps to ensure their long-term success.
SWOT analysis is also a useful tool for decision-making. By evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of various options, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their objectives and values. For example, if an organization is considering expanding into a new market, they can use SWOT analysis to evaluate the potential risks and benefits of that expansion.
Limitations of SWOT analysis
However, there are also some limitations to SWOT analysis that organizations should be aware of. One of the main limitations is that it is a subjective process that relies on the opinions and perspectives of the team conducting the analysis. This means that different teams may come up with different results based on their individual biases and experiences.
Another limitation is that SWOT analysis does not provide a clear roadmap for implementation. While it is useful for identifying issues and developing strategies, it does not provide a step-by-step plan for implementing those strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SWOT analysis is a powerful tool that organizations can use to evaluate their internal and external factors, identify their strengths and weaknesses, and develop strategies to achieve their objectives. While it has some limitations, it is a useful tool for decision-making and can help organizations to stay competitive in an ever-changing business environment.
